Learn what crawl budget is, why it matters for SEO, and how to optimize it to insure Googlebot focuses on your most important runners. Includes tools, tips, and FAQs.
As a marketer, you’ve spent hours adding value to your website. Now imagine a caller drops by regularly to check what’s new and decide what’s worth showing in Google Hunt.
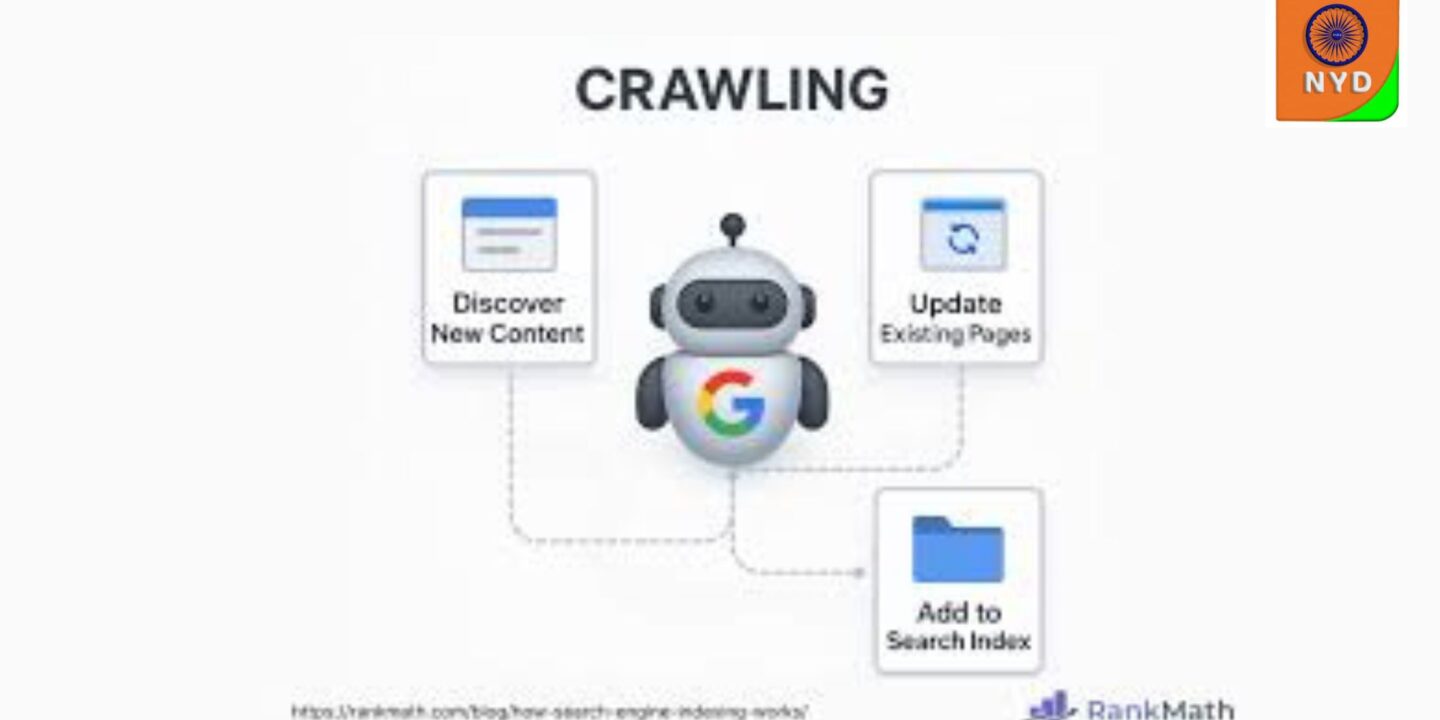
That caller? It’s called Googlebot, and it’s the straggler responsible for discovering and recording your content. It scans your runners to decide what should be included in Google Hunt and how frequently to return for updates.
But Googlebot does n’t have unlimited coffers to always crawl in- depth. Each point gets a set crawl budget, or an allowance of time and bandwidth for Googlebot to spend exploring your point.
The more efficiently you use your crawl budget, the easier for Googlebot to find and prioritize your most precious content which can help you rank.
Let’s launch with the basics What’s crawl budget, and why does it count?
What is crawl budget (and why does it matter)?

Crawl budget is the limit that Googlebot has for how numerous runners it’s willing to “ crawl ” on your website in a given timeframe.
Think of Googlebot as having a set quantum of time and energy each day to explore your point. It flips through your point’s runners, deciding what to read and what to skip.
still, 000 URLs but Googlebot only has the energy to crawl 2, 000 moment, If your point has 10. And you want it to prioritize the right effects because without guidance, Googlebot might waste time on low- value runners.
rather of indexing your rearmost blog post or your new crusade wharf runner, it could get wedged crawling 300 nearly identical sludge URLs.
Let’s say you run an online shop with 6,000 runners. Now imagine half of those runners are variations — color pollutants, size options, slight duplicates.
To a client, those variations are useful. But to Googlebot, they’re substantially the same.
So while it’s busy crawling
product/ red
product/ blue
product/ xl
It might skip runners like
Your recently streamlined homepage
A new seasonal wharf runner
Your rearmost blog post that’s formerly getting traction on socials
Indeed if the content is ready, the most important runners might not be crawled — or listed — soon enough. All because your crawl budget was spent away.
Crawlability vs. crawl budget What’s the difference?
Crawlability and bottleneck budget sound analogous, but they’re not the same thing.
Why crawl budget matters—and when it actually applies to your site

Both matter because without access and precedence, indeed your stylish runners can go unseen by Google, and noway show up in hunt.
- Crawlability = Access Crawlability answers a simple question Can Googlebot access this runner? still, it wo n’t crawl the runner, no matter how important it is, If the answer is no. Example It still exists, but Googlebot sees that block as a “ Do n’t enter ” sign. It skips the runner entirely, freeing up crawl budget for other areas.
- Crawl budget = Priority and choice Crawl budget comes after crawlability. It’s no longer “ Can I crawl this runner? ” — it’s “ Do I’ve the time and energy to crawl this runner soon? ” Indeed if a runner is crawlable, Googlebot might decide it’s not worth its limited attention right now. Example You’ve got a crawlable event runner from 2017 that’s still live. It is n’t blocked, but it’s outdated and gets no business. Googlebot might suppose “ Hmm. Not critical. I’ll come back to it ultimately. ” So indeed though the runner is crawlable, it might go untouched for months. In the case of crawlability vs crawl budget, which should you use? You need both crawlability and crawl budget to work together. still, it wo n’t be discovered, If a runner is n’t crawlable. still, it might be ignored until it’s too late, If it’s crawlable but low precedence. This helps show how they’re related, but not exchangeable. still, it ca n’t rank it, If Googlebot has n’t crawled your runner. It might not indeed know it exists or worse, it could be showing an outdated interpretation in hunt results. Your crawl budget decides whether Google sees your runner and when, which has everything to do with your chances of showing up( and showing up well) in hunt. For illustration, if you launch a new product runner that has n’t been crawled, it wo n’t appear in hunt. Or if you’ve streamlined pricing across service runners but Googlebot has n’t had a chance to recrawl, druggies might still see outdated prices in the SERP. This is where crawl budget gets serious.
When crawl budget becomes a real concern
While crawl budget affects every point, it’s especially critical for
Large websites spots with thousands or millions of URLs
News and media New URLs post constantly and need fast indexing
Ecommerce spots Tons of product pollutants, variations, and orders
still, your most important or time-sensitive content might be the very thing that gets missed, If Googlebot ca n’t keep up.
Running a lower point?
Larger spots are more delicate to manage, including from a crawl perspective.However, 000 indexable URLs, crawl budget likely is n’t your main issue, If your point has smaller than 500 – 1. Googlebot can generally handle small andmid-sized spots with ease, crawling all the corridor of your point.
In these cases, concentrate on what’s blocking indexing, not crawling. Common culprits include
runners blocked by noindex or canonical markers
Weak internal linking
Thin, indistinguishable, or low- quality content
How Google calculates your crawl budget
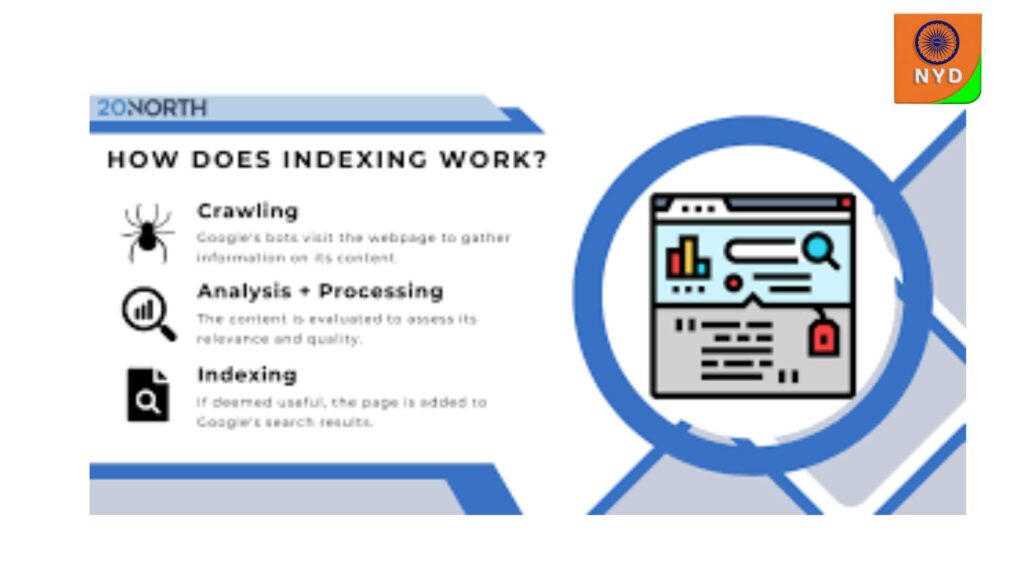
Google looks at two main factors when deciding what, and how important, to crawl
Crawl Demand How important Google wants to crawl from your point.
Crawl Capacity Limit How important your garçon can handle without performance issues.
Let’s look at what shapes them.
What drives crawl demand
Crawl demand reflects how precious or fresh Google thinks your content is. With limited coffers, it prioritizes runners that feel worth its time.
Then’s what affects that demand
Perceived force
This is how numerous runners Google thinks you actually have.
still, 000 URLs, but internal links only expose 3, If your sitemap says 40.
That means big portions of your point could go uncrawled, especially if your new or seasonal content lives on those hidden runners.
Fashionability
runners with backlinks or strong engagement signals tend to get crawled more frequently.
still, Googlebot will probably visit it regularly, If your blog post goes viral or picks up backlinks.
But if an old press release is buried deep in your point armature, it might be ignored for months.
Staleness
Google does n’t want to waste time checking the same banal runner over and over.
still, it drops in crawl precedence, If a runner has n’t changed in times.
But if you constantly modernize product rosters, refresh blog posts, or revise wharf runners, Google will return more frequently to keep up.
What limits Google from crawling your point
Indeed if Google wants to crawl everything, it wo n’t if your point shows signs of insecurity. There are generally two crucial sources of crawl budget issues.
Crawl health
still, timing out, or returning garçon crimes, If your point is slow.
Indeed modest crawling can decelerate druggies down on participated or underpowered hosting, commodity Google laboriously tries to avoid.
Google’s crawl limits
Google also sets internal limits on how important it’s willing to crawl from a sphere.
It’s a balancing act if either demand or capacity is low, crawl budget drops.
Think of it like a formula
Crawl Demand × point Capacity = Your Crawl Budget
still, your point’s crawl budget shrinks, If either side of that equation decreases.
Crawl signals: How to influence what Googlebot priorities
Google does n’t just crawl everything on your point inversely. It prioritizes runners that feel precious, streamlined, or in demand.
Several signals impact whether and how frequently Google crawls a runner. Some say “ skip this, ” while others flag content as important.
Signals that impact crawl budget
So, what exactly tells Google whether to pay attention to a runner or skip it?
These signals behind the scenes shape how your crawl budget gets spent.
This is a simple textbook train that sits in the root of your website. It tells Googlebot what not to crawl.
So if you block a runner then, Google wo n’t waste any crawl budget trying to reach it. It’ll just move on.
Example You might block your admin login runner or thank- you runners after a form is submitted.
Noindex markers
This is a bit different. A noindex label tells Google, “ You can crawl this runner, but do n’t show it in hunt results. ”
Google might still crawl it, but if it sees that noindex signal over time, it might decide not to crawl it much at each, since it’s not useful for hunt.
illustration A staging interpretation of a wharf runner that’s not ready to go live.
Canonicals
Canonicals tell Google which interpretation of analogous runners to treat as primary, precluding crawl budget waste across duplicates. So if you’ve got loads of near-identical performances( like product pollutants or UTM- tagged URLs), a canonical says “ Hey, treat this interpretation as the real deal. ”
still, ” but they all show analogous particulars, you can set a canonical label to point back to the main “ pink shoes ” runner, If you have five filtered product runners for “ pink shoes under$ 20.
That way, you’re not wasting bottleneck budget on all the lookalikes.
Sitemap entries
A sitemap is like a treasure chart of your point. It tells Google “ These are all the crucial runners I want you to know about. ”
still, well- structured, and streamlined regularly, If your sitemap is clean.
Make sure your sitemap includes your blog posts, main product runners, and crucial orders — not broken runners or expired URLs.
Internal linking depth
This just means how numerous clicks does it take to get to a runner from your homepage? If it takes six to seven clicks to find a runner, Google might suppose “ This runner must n’t be that important since it’s not fluently accessible for guests. ”
Example Pages linked directly from your homepage, footer, or main menu tend to get crawled further than bones
buried deep outside subfolders.
Quick comparison
A product runner with glowing reviews, good backlinks, and a lot of internal links? Likely to be crawled frequently.
A filtered interpretation of that same runner for “ pink speakers under$ 20, ” with no links and indistinguishable content? Might slightly get a regard.
What wastes crawl budget (and how to fix it)
Think about it like this: googlebot is flipping through the pages of your internet site with constrained energy. the more it wastes on low-value pages, the less it spends to your top content.
Before we get into the largest move slowly budget wasters, it’s worth running a brief web page audit to look if any of those problems are already showing up in your web page.
So permit’s have a look at the biggest offenders, a way to spot and stop them.
- duplicate pages
These are extraordinary urls that display the precise same or very similarContent material.
All the ones pages may look the equal to someone, however to googlebot? they’re separate pages. so it reads the same content over and over.
Laborious, proper?
Why it’s a problem: google is spending power crawling versions of the equal factor rather than the usage of that strength on new or updated content material.
The way to repair it:
Use canonical tags to factor to the primary model of the page.
Or, if the page isn’t important? set it to noindex so google doesn’t hassle in any respect.
Consider canonicals as a gentleNudge pronouncing, “hiya, this version’s the one that topics.”
- damaged hyperlinks and soft 404s
Those are pages that not exist however nevertheless seem for your internal links or xml sitemaps.
Examples: a deleted product page that also lives to your sitemap or a weblog hyperlink that returns a indistinct “sorry, web page not observed” message (aka a soft 404).
Why it’s a problem: google will keep looking to go to these pages like knocking on a door that’s now not there. time and again.
A complete waste of time.
A way to fixIt:
Clean up your internal hyperlinks and remove some thing that leads nowhere.
Set up 301 redirects to ship google (and visitors) to a helpful opportunity as an alternative.
To your sitemap, handiest listing stay, useful pages.
Think of it like tidying up the hallways so google doesn’t keep bumping into locked doorways.
Three. orphan pages
Those include pages that exist, but nothing hyperlinks to them. they’re floating round your website and not using a clean way in, nearly like a ghost floating round your internet site.
Example: an oldBlog post from 2019 that has no hyperlinks from your homepage, no category web page, and no tags. just… misplaced.
Why it’s a hassle: google might come across it eventually, but it’s the use of crawl budget on a web page that’s not assisting your website online in any way.
A way to fix it:
Make sure each page is linked to from somewhere beneficial—whether or not it’s your major nav, a footer, or some other associated article.
Or, if the page is surely old or vain? take into account doing away with it or placing it to noindex.
No person likes to be overlookedIn the bloodless. help google locate your content with proper links.
Four. faceted navigation
Those endless mixtures of filters or kind orders—assume length, colour, rate, class—generate heaps of barely one-of-a-kind urls.
Examples:
/footwear?colour=blue&size=7&sale=genuine
/footwear?length=7&sale=real&coloration=blue (yes, that counts as some other web page)
Why it’s a hassle: googlebot gets stuck in a loop. it continues crawling tiny versions in url parameters displaying the same products, wasting price range on pages thatProvide nothing new.
A way to restoration it:
Block these urls in your robots.txt so google doesn’t even try to crawl them
Use parameter settings in google seek console to inform google which filters to ignore
Canonical again to the primary product class web page, wherein feasible
Consider this as final the door on an limitless maze. by means of doing so, you’re supporting google get to the good things quicker.
How do you check crawl activity?
After you understand crawl price range, the next step is tracking it. google seek console(gsc) offers you direct perception into how googlebot interacts along with your site.
This device gives you a at the back of-the-scenes look at how google is crawling your web site:
How often it visits
What styles of pages it’s fetching
Whether your server is maintaining up
We’ll stroll via where to locate this data and what each element way.
- gsc move slowly stats evaluate
To get began, head over in your gsc property and:
Click on “settings” in the sidebar
Scroll down to the crawling phase
Click on “open report”
You’llNow be in the move slowly stats report. this is in which the great things lives.
From right here, you’ll get a ninety-day photo of google’s move slowly interest across your site, inclusive of any red flags or adjustments well worth noting. consider it as a touch health test on your crawl price range.
How do in case you’re hitting your move slowly budget restrict?
One commonplace sign is a high variety of pages in google seek console marked as:
“observed – presently now not listed”
“crawled – presently no longer listed”
These signals advocateGoogle is aware of the pages exist, however hasn’t prioritized them for crawling or indexing but.
Right on the pinnacle, you’ll see a visible chart of crawl interest over the past 90 days. this enables you notice any patterns or surprising drops or spikes in crawling. and under the chart, you’ll see 3 key stats:
Overall move slowly requests: if this drops, google may be deprioritizing your website online
Overall download size: excessive values may also signal bloated pages or media
Average response time: rising numbers suggest serverSlowdowns
Three. host fame
This element shows you the way properly your site is dealing with google’s crawling, specially from a technical or server perspective.
If the whole thing’s easy, you’ll see something like: “hosts are wholesome.”
If now not, you may get a caution like: “hosts had problems in the beyond.”
Click into the box to find greater info. you’ll see:
Robots.txt fetch troubles: e.g. google couldn’t load your robots.txt file
Dns troubles: issues resolving your domain name
Server connectivity troubles:Your server didn’t respond speedy enough (or in any respect)
Why it matters: if google can’t reach your web page reliably, it’ll move slowly less regularly. you’ll need to address any of these issues speedy.
- crawl requests breakdown
That is the absolutely meaty bit. google breaks down what it’s crawling, how, and why. you’ll see 4 available classes:
By response code
This indicates how your pages spoke back—200 good enough, 404 now not determined, 301 redirect, and so on.
Instance: in case you’re seeing loads of 404s here, you may have damagedLinks wasting crawl budget.
Through document type
Googlebot doesn’t just move slowly pages in html. it additionally grabs pictures, scripts, and css.
Instance: if a bit of your move slowly price range goes closer to javascript documents, that might be well worth optimizing or restricting.
By means of purpose of the request
Google labels each request by way of motive: discovery (finding new pages) or refresh (checking returned on recognised pages).
Instance: seeing usually “refresh” would possibly mean you’re now not publishing a good deal new content proper now, or google isn’tAware of it.
By using googlebot type
Google makes use of extraordinary bots for jobs, like googlebot, cellphone, and photo.
Example: in case you see lots of requests from googlebot smartphone, google is prioritizing the cellular model of your website (that’s first-rate).
Clicking into any item indicates you specific pages that suit that type, like which urls again a 404 or which ones had been crawled by a selected bot.
Google seek console offers you the fundamentals instantly from the supply.
Those help discover how googlebotBehaves over time, in which it’s spending crawl finances, wherein it’s losing off, and which sections of your website online may be undercrawled. you can fast pinpoint opportunities for move slowly finances optimization.
You don’t want to grasp move slowly finances nowadays, but it does play a key position in how your content material receives discovered and ranked. whilst search engines focus on the right pages, you’re much more likely to reveal up in which it counts.
Crawl finances enables google prioritize your most precious content.Make certain it’s operating on your desire.
Start with the aid of checking what’s already visible. use our serp checker to look which pages are ranking and which ones aren’t. this will help you notice ignored opportunities and make your virtual marketing efforts greater effective.Think about it like this: googlebot is flipping thru the pages of your internet site with confined energy. the extra it wastes on low-value pages, the much less it spends on your top content.
Earlier than we get into the most important move slowly budget wasters, it’s really worth walking a short web site audit to look if any of these troubles are already showing up to your site.
So allow’s look at the biggest offenders, a way to spot and stop them.
- replica pages
Those are exclusive urls that display the precise equal or very similarContent.
All those pages may look the same to a person, but to googlebot? they’re separate pages. so it reads the identical content material time and again.
Laborious, proper?
Why it’s a problem: google is spending electricity crawling variations of the equal component rather than the usage of that energy on new or updated content.
A way to fix it:
Use canonical tags to factor to the principle version of the web page.
Or, if the web page isn’t critical? set it to noindex so google doesn’t trouble at all.
Think about canonicals as a mildNudge pronouncing, “hi there, this version’s the one that subjects.”
- damaged hyperlinks and gentle 404s
Those are pages that no longer exist but nevertheless appear to your internal hyperlinks or xml sitemaps.
Examples: a deleted product web page that also lives in your sitemap or a blog link that returns a indistinct “sorry, web page no longer discovered” message (aka a soft 404).
Why it’s a hassle: google will keep trying to go to these pages like knocking on a door that’s now not there. again and again.
A complete waste of time.
How to restoreIt:
Smooth up your internal hyperlinks and dispose of whatever that leads nowhere.
Set up 301 redirects to ship google (and visitors) to a helpful opportunity instead.
In your sitemap, handiest list live, beneficial pages.
Consider it like tidying up the hallways so google doesn’t hold bumping into locked doors.
- orphan pages
Those encompass pages that exist, but not anything hyperlinks to them. they’re floating round your web site with no clear manner in, nearly like a ghost floating round your website.
Example: an oldWeblog publish from 2019 that has no links out of your homepage, no category page, and no tags. simply… misplaced.
Why it’s a problem: google may come across it in the end, but it’s the usage of move slowly finances on a page that’s no longer helping your web site in any manner.
How to repair it:
Make sure each web page is linked to from somewhere beneficial—whether it’s your important nav, a footer, or any other associated article.
Or, if the page is truly old or useless? don’t forget putting off it or placing it to noindex.
No one loves to be omittedInside the cold. help google locate your content with right hyperlinks.
Four. faceted navigation
Those infinite combos of filters or type orders—suppose length, shade, charge, category—generate hundreds of barely specific urls.
Examples:
/footwear?color=blue&size=7&sale=actual
/shoes?size=7&sale=actual&coloration=blue (sure, that counts as every other page)
Why it’s a trouble: googlebot gets caught in a loop. it continues crawling tiny variations in url parameters displaying the equal merchandise, losing price range on pages thatProvide not anything new.
The way to restore it:
Block these urls to your robots.txt so google doesn’t even try to move slowly them
Use parameter settings in google search console to inform google which filters to disregard
Canonical lower back to the principle product class page, in which feasible
Consider this as ultimate the door on an infinite maze. by way of doing so, you’re supporting google get to the good things quicker.
Want to see what Google’s seeing?
You don’t want to grasp crawl finances today, however it does play a key position in how your content gets located and ranked. whilst search engines attention at the proper pages, you’re much more likely to expose up wherein it counts.
Move slowly price range allows google prioritize your most valuable content.Make sure it’s operating to your desire.
Begin with the aid of checking what’s already visible. use our serp checker to see which pages are ranking and which of them aren’t. this may assist you see ignored opportunities and make your digital advertising efforts greater powerful.











