
GitHub Activities is a ceaseless integration and ceaseless conveyance (CI/CD) stage that permits you to robotize your construct, test, and sending forms. For case, you can make workflows that construct and test each drag ask to your store. Once it’s combined you can convey it.
But it goes past that and lets you run workflows when other occasions happen in your store. For case, you can run a workflow to consequently include the suitable names at whatever point somebody makes a modern issue in your repository.
But to begin with, some time recently running the workflow we require a few compute assets. These are called runners. GitHub gives Linux, Windows, and macOS virtual machines to run your workflows, or you can have your claim self-hosted runners in your possess information center or in the cloud.
What Is GitHub Actions?
GitHub Activities is a stage for persistent integration / nonstop conveyance (CI/CD). It empowers you to robotize construct, testing, and sending pipelines. It too lets you run self-assertive code on a indicated store when an occasion happens. Activities employments code bundles in Docker holders that run on GitHub servers. They are congruous with all programming dialects to guarantee you can run them on open clouds as well as neighborhood servers. This is portion of an broad arrangement of guides almost CI/CD.
GitHub Actions Architecture and Concepts
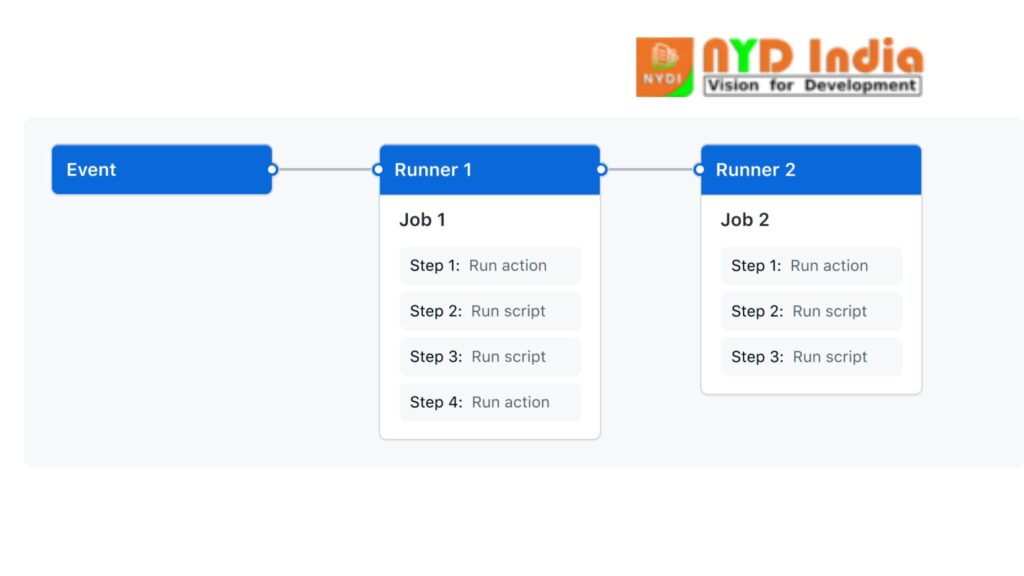
GitHub Activities permits you to arrange your workflow to be activated once a particular occasion happens in the store. For case, when an issue is made or when a drag ask is opened.
A workflow contains one or a few occupations running in parallel or successive arrange. Each work runs interior a holder or in a isolated virtual machine (VM) runner. Also, each work incorporates one or a few steps that run a predefined script or an activity, a reusable expansion that disentangles your workflow.
GitHub Actions Workflows
A GitHub Activities workflow is an mechanized handle that runs one or a few employments. You can design workflows by characterizing a YAML record, which is checked into the store. This record runs when:
1.Triggered by a particular occasion in the repository
2.Triggered manually
3.At a predefined schedule
You can discover workflow definitions in the .github/workflows registry of each store. A store can incorporate a few workflows, each performing diverse assignments. You can utilize, for case, one workflow for building and testing drag demands, another workflow for conveying the application at whatever point a discharge is made, and an extra workflow for including a name at whatever point a modern issue is opened.
GitHub Actions Events
An occasion is a particular movement in a store that triggers a workflow run. For illustration, movement can start from GitHub when somebody makes a drag ask, opens an issue, or pushes a commit to a store. You can moreover trigger a workflow run on a plan, by posting to a REST API, or manually.
Workflow Triggers
A workflow trigger is an occasion that causes a workflow to run. Here are workflow trigger examples:
1.Events happening in the workflow’s repository
2.Events happening exterior of GitHub and trigger a repository_dispatch occasion on GitHub
3.Manual
4.Scheduled times
For occasion, you can arrange a workflow to run once a thrust is made to a default store department, once an issue is opened, and once a discharge is created.
GitHub Actions Jobs
A work in GitHub Activities is a arrangement of workflow steps that run on a single runner. The steps can incorporate activities to run or shell scripts for execution. Activities execute each step in arrange, as all steps in a work are forbid. It executes each step on the same runner, empowering information sharing between steps. For occasion, if you have a step to construct an application, there might be a ensuing step to test the recently built application.
Jobs don’t have conditions by default, but you can arrange occupations to be subordinate on other employments and run in grouping. Something else, the employments will execute in parallel. If a work has a reliance on another work, it must hold up for that work to total some time recently running. There may be a few construct occupations, each for a distinctive design, without any dependencies—however, a bundling work would be subordinate on these occupations. The non-dependent construct occupations run at the same time, but the bundling work can as it were run when all the construct employments are complete.
GitHub Actions Matrix
You can utilize a lattice methodology to run numerous related occupations based on the same work definition. Distinctive combinations of factors in the work definition naturally make diverse work runs. For occasion, a network might be valuable for testing code on distinctive working frameworks or in diverse forms of a programming language.
Actions
Actions are custom applications for GitHub Activities that perform complex but monotonous assignments. You might utilize activities to maintain a strategic distance from composing as well much dreary code in a workflow. An activity may drag a store from GitHub, set up confirmation measures to the cloud supplier, or arrange the right toolchain for the improvement environment.
You can type in an activity from scratch or utilize an existing activity accessible from the GitHub Commercial center in your workflow.
Runners
Runners are machines that have the GitHub Activities runner app introduced. They hold up for accessible occupations to execute. Once a runner picks up a work, it runs the activities indicated by the work and reports the comes about to Github. You can have runners on your claim server or machine or utilize GitHub-hosted runners.
Workflow Dependency Caching
A workflow run can reuse the yields and conditions from other runs. Reliance and bundle administration devices like Maven, npm, Yarn, and Gradle keep nearby caches of all downloaded dependencies.
Each work on a GitHub-hosted runner begins in a new environment, so it is fundamental to download the conditions for each unused work. These downloads can stretch the runtime, increment organize utilization, and increment costs. GitHub permits you to quicken the prepare of reproducing reliance records by caching as often as possible utilized records in a workflow.
You can cache work conditions by utilizing the cache activity in GitHub. This activity builds and reestablishes caches distinguished utilizing special keys.
CI/CD with GitHub Actions
GitHub Action supports continuous integration and deployment.
Continuous Integration with GitHub Actions
Continuous integration is a program advancement hone that includes visit commits to a shared code store. GitHub Activities gives nonstop integration (CI) workflows that can construct code in the store and execute tests. A workflow can run on a GitHub-hosted VM or a self-hosted machine.
You arrange CI workflows to run in reaction to particular GitHub events—for occurrence, when a engineer pushes unused code to the store. You can too utilize the store alacrity webhook to plan workflows or set triggers based on outside events.
GitHub runs the CI tests, giving the comes about for all tests in a drag ask. It lets you see any blunders presented to the department by each alter. Once a alter has passed all the CI tests in the workflow, it is prepared for survey by group individuals, and you can blend it into the store. If the commit comes up short a test, it is an sign of a breaking alter.
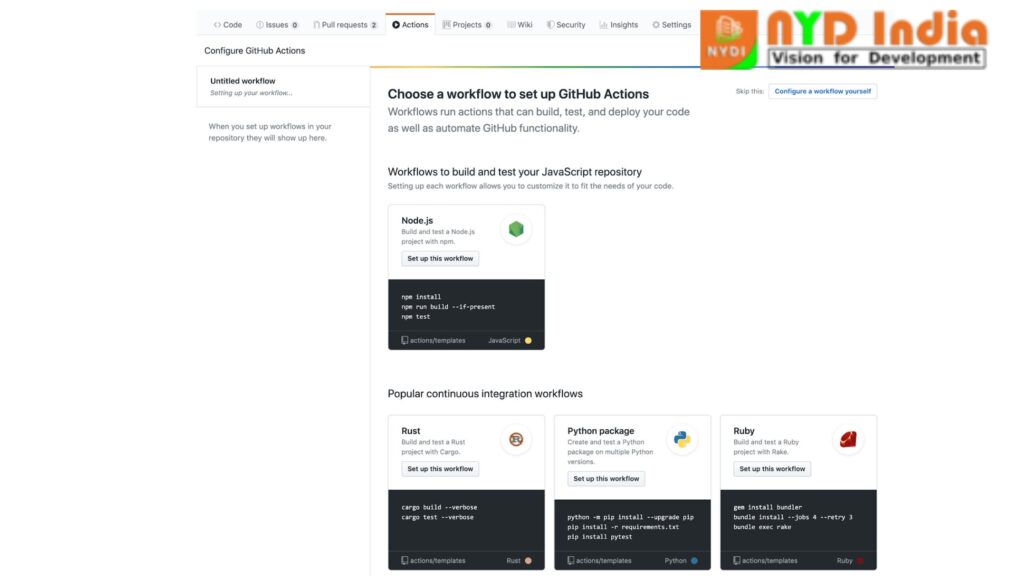
When setting up persistent integration in the Git store, GitHub will analyze your code and prescribe particular CI workflows based on your repository’s system and dialect. For occurrence, GitHub recommends starter workflows that introduce the suitable bundles and run the tests (i.e., a Node.js bundle if you are utilizing Node.js). You can utilize the GitHub-recommended starter workflow as is, customize it to your needs, or make a unused custom workflow to run the ceaseless integration tests.
GitHub Activities makes a difference you set up a CI workflow for your improvement extend and can make workflows for the whole SDLC. You seem set up activities to bundle, send, and discharge a extend.
Continuous Deployment with GitHub Actions
Continuous arrangement is an expansion of nonstop integration and conveyance that mechanizes the prepare of distributing and sending program discharges. A CI/CD instrument regularly builds and tests the code naturally some time recently conveying it as portion of the ceaseless sending handle.
You can design GitHub Activities workflows to send program items. A workflow can confirm that the code capacities as anticipated by building the code in the store and running tests some time recently deployment.
You can plan CD workflows to run in reaction to particular GitHub occasions, such as a engineer pushing code to the repository’s default department of your store. Then again, workloads can run on set plans, when activated physically, or in reaction to outside events.
GitHub Activities offers a few highlights to offer assistance you control your organizations. Situations permit you to piece occupations until they get endorsement, confine the branches that can trigger workflows, or limit get to to insider facts. Concurrency lets you constrain the CD pipeline to one in-progress and one pending sending at a time.
GitHub Actions Quick Start Tutorial
Using GitHub Activities requires a GitHub store. The employments in a workflow can naturally execute activities related to the store and associated with the repository’s code as well.
Create Workflow
To create workflows in GitHub Actions:
1.Create a modern registry in your store and title it .github/workflows if such a catalog doesn’t as of now exist.
2.In the modern registry, press the Include Record button on the top-right side of the window and select Make unused record. Title the recently made record demo-github-actions-workflow.yml
3.Paste the taking after code in the demo-github-actions-workflow.yml
4.Click the Propose modern record to make a pull-request for committing this record to the store.
5.Go to the foot of the page and select the Make a modern department for this commit and begin a drag ask option.
6.Go to the repository’s primary page and press Activities on the bar beneath the store name.
View Results of Workflow
To see the results after running a GitHub Actions workflow:
1.A sidebar on the cleared out appears all the workflows on the page that opens. Press the one that shows Demo-GitHub-Actions-Workflow, the title of the workflow made for this tutorial.
2.The list in the center appears the workflows that have run. Select the one that shows Make demo-github-actions-workflow.yml to see the comes about of the one made in the past segment, Make Workflow.
3.Under the sidebar on the cleared out that shows Occupations, select the one showing Discover-GitHub-Actions-Workflows.
4.The log that opens appears each step of the workflow and what yield it caused.
5.The steps for the resound explanations in the workflow appear the factors supplanted with their particular values. Press on a step that shows List records in the store, and it appears the records show in the repository.
6.An action’s virtual machine has tall transfer speed and is moderately quick, but complex activities take longer to set up and execute, coming about in more time went through holding up. GitHub Activities has restricted virtual machine plans—the free arrange has a cap of 2000 free minutes in a given month.
GitHub Actions Best Practices
Here are some tips for using GitHub Actions.
Use Minimal Actions
When setting up a workflow or activity, you might not feel that a few seconds make a enormous difference—however, these seconds include up depending on the occasions activating the activities and workflows. An imperative best hone when making unused activities is to attempt to keep them as negligible as possible.
For occasion, you ought to utilize light Docker pictures for activities that run in containers—e.g., snow capped, alpine-node. Keep the establishments to a least to decrease the action’s running time from boot to completion.
Keeping activities light is critical in any case of whether you make a standalone activity or a full CI/CD workflow. GitHub Activities sets up and runs each activity in a clean environment for each run, so it has to download and introduce all the conditions each time.
Another way to diminish the running time is to dodge introducing or downloading conditions wherever conceivable. You can utilize a few strategies to minimize reliance downloads, in spite of the fact that these are all based on two fundamental techniques.
Avoid Unnecessary Dependency Downloads
The to begin with approach is to distribute an whole hub module organizer. This technique is appropriate for distributing standalone activities in Node-based ventures. The moment approach is to use the caching component in GitHub wherever conceivable. This technique is appropriate for standalone activities as well as activities running inside a CI workflow.
Store Authorship Details in the Action Metadata
You can energize creators of activities to take possession of their code by indicating the activity creator in the metadata—this information dwells in a YML record characterizing the activity. This metadata can incorporate numerous subtle elements almost each activity, counting its required inputs, branding, section point, yields, and creator.
There are two primary utilize cases for counting the action’s creator in the metadata record. To begin with, when you have open activities, it is critical to trait each activity to the redress creator. In expansion to giving creators credit for their work, it permits others who are utilizing the activities to distinguish and allude to the creator with any questions.
The moment utilize case applies to private activities with an organization. The issue of credit is less important since no one exterior the company will see it. In any case, the inside group still needs to know who is capable for each action—the creator keeps up and answers questions approximately the activity.
Combine GitHub Actions with Codefresh to Support GitOps and Kubernetes Deployments
GitHub activities is a exceptionally effective stage but it is centered generally on CI and does not bolster GitOps and local Kubernetes organizations. Codefresh is made particularly for GitOps and Cloud local applications and incorporates local back for utilizing GitHub Activities for the CI portion of the Computer program lifecycle.
This implies that you can get the best of both universes by keeping all your CI workflows in GitHub Activities, whereas utilizing Codefresh for progressed highlights such as:
1.Application dashboards
2.Git source managements
3.Configuration float management
4.Kubernetes environment dashboards
5.Topology views
In case you are modern to Codefresh – we have made it our mission since 2014 to offer assistance groups quicken their pace of advancement. Codefresh as of late discharged a totally revamped GitOps CI/CD toolset. Fueled by Argo, Codefresh presently combines the best of open source with an enterprise-grade runtime permitting you to completely tap the control of Argo Workflows, Occasions, CD, and Rollouts. It gives groups with a bound together GitOps involvement to construct, test, send, and scale their applications.











